Durée
6 semestres
Composante
UFR Droit, Economie, Gestion, Observatoire des Sciences de l'Univers en région Centre
Lieu(x)
Orléans
Présentation
Le Cycle Pluridisciplinaire d'Études Supérieures (CPES) est un cursus diplômant d'excellence en trois années associant l'Université d'Orléans et un lycée doté de classes préparatoires (Lycée Pothier). Outre sa sélectivité, la spécificité de cette formation réside à la fois dans le partage des enseignements entre des enseignants de classes préparatoires et des enseignants-chercheurs de l'université, ainsi que par sa pluridisciplinarité, en associant les géosciences à l'économie.
L'objectif est de proposer aux étudiants une formation leur permettant d'acquérir une triple compétence face aux grands défis d'aujourd'hui et de demain. Le positionnement stratégique de ce CPES sur les problématiques associées aux dérèglements climatiques, aux transitions (écologique, climatique, énergétique) ainsi qu'aux enjeux économiques à l'ère du Big Data en fait une formation unique d'excellence.
La science des données et le numérique constituent le fil rouge de cette formation, afin notamment d'appréhender le plus justement possible l'impact des activités humaines en tirant profit de la disponibilité grandissante des données.
Les enseignements assurés par les enseignants de classes préparatoires permettront aux étudiants d'acquérir un socle de connaissances et de compétences fondamentales pour le suivi d'enseignements de pointe à l'université, irrigués par les travaux de recherche les plus récents en la matière qui y sont menés. Pour cette raison, les enseignements sont majoritairement réalisés au lycée la première année (80 %), à parts égales entre lycée et université la deuxième année, puis essentiellement à l'université en troisième année (80 %).
Les enseignements sont structurés en trois grands blocs, chacun visant à développer une compétence inter-connectée aux deux autres :
• Bloc Économie/Sciences des données
• Bloc Géosciences et ressources naturelles
• Bloc fondamental (mathématiques, statistique, probabilité, numérique, anglais, …)
A l'issue de la deuxième année, les étudiants s'orientent vers l'un des deux parcours proposés par le CPES :
• Parcours Modélisation économique et environnement, piloté par Orléans School of Economics, permettant l'obtention d'une Licence d'Économie-Gestion,
• Parcours Observation, mesure, sciences expérimentales et numérique, piloté par l'Observatoire des Sciences de l'Univers en Région Centre-Val De Loire (OSUC), permettant l'obtention d'une Licence Sciences de la Terre.
Compétences
Cette formation ambitionne de développer une triple compétence chez les étudiants :
1) En sciences économiques :
Les dérèglements climatiques et la raréfaction des ressources naturelles créent et créeront des besoins croissants d'experts en gestion des ressources et politiques des transitions (écologique, climatique, énergétique, …). Des compétences accrues d'analyse, de modélisation, de gestion et de traitement des données ainsi que des connaissances solides sur les phénomènes à l'origine des transitions environnementales deviennent ainsi indispensables pour les futures générations d'économistes. Afin de faire face à ces transformations majeures, le programme délivre des enseignements fondamentaux (microéconomie, macroéconomie, politiques économiques, économétrie…) et thématiques (économie de l'environnement, croissance, enjeux de la transition écologique, finance verte, microéconomie des ressources naturelles…) qui permettront de former une nouvelle génération d'experts outillés pour faire face à ces mutations, capables de les comprendre et de les analyser
2) En géosciences :
Les progrès des instrumentations et des techniques d'observation permettent aux scientifiques de recueillir chaque année des données de plus en plus détaillées, étendues et volumineuses. Ces données alimentent nos capacités de prédiction de l'évolution du système Terre, lui-même indispensable à la gestion des futures transitions environnementales. Des compétences en termes d'acquisition, d'analyse, de gestion et de traitement des données deviennent ainsi indispensables pour les générations futures de géoscientifiques souhaitant relever les nombreux défis de ces transitions. Notre programme de formation CPES délivre les enseignements théoriques et pratiques qui permettront aux étudiants de se spécialiser ensuite sur l'ensemble des filières des géosciences nécessitant d'allier des compétences d'observation de terrain, d'acquisition de données, de leur gestion et de leur traitement jusqu'à leur modélisation numérique haute-performance.
3) En numérique et science des données :
Pour répondre à la fois aux besoins des entreprises et administrations en pleine ère du Big Data, le CPES offre un avantage significatif à nos étudiantes et étudiants qui voudront poursuivre leur spécialisation dans des domaines nécessitant de comprendre, gérer et modéliser de nombreuses sources de données. Le programme de formation se concentre ainsi sur le développement de compétences numériques appliquées directement aux problématiques environnementales, abordées à la fois sous le prisme des géosciences et celui de l'économie, en intégrant les techniques les plus récentes, telles que l'IA.
Des enseignements fondamentaux en mathématiques, statistique, probabilité, méthodologie scientifique ou encore en anglais viennent également irriguer l'ensemble de la formation. Une place importante est consacrée aux projets tutorés, intégrés aux laboratoires de recherche associés à l'UFR DEG et à l'OSUC, afin de développer, en plus de savoirs, de véritables savoir-faire chez l'étudiant.
Contacts utiles
Bureau des relations internationales de l'UFR DEG :
https://www.univ-orleans.fr/fr/deg/international
international.deg[at]univ-orleans.fr
Tél : +33(0) 2 38 49 47 30
ORIENTATION ET
INSERTION PROFESSIONNELLE
DOIP
02 38 41 71 72
doip@univ-orleans.fr
Programme
Au cours des deux premières années, les étudiants reçoivent des enseignements fondamentaux, ainsi que des enseignements spécifiques à l'économie, aux géosciences et à la science des données. Le CPES se scinde en deux parcours à l'issue de la deuxième année, l'un axé davantage sur l'économie, l'autre sur les géosciences.
Une partie des enseignements est dispensée au Lycée Pothier. L'autre partie est dispensée sur le campus universitaire.
3 blocs de formation à volumes horaires équivalents :
-
Sciences économiques
-
Géosciences et ressources naturelles
-
Fondamentaux du numérique
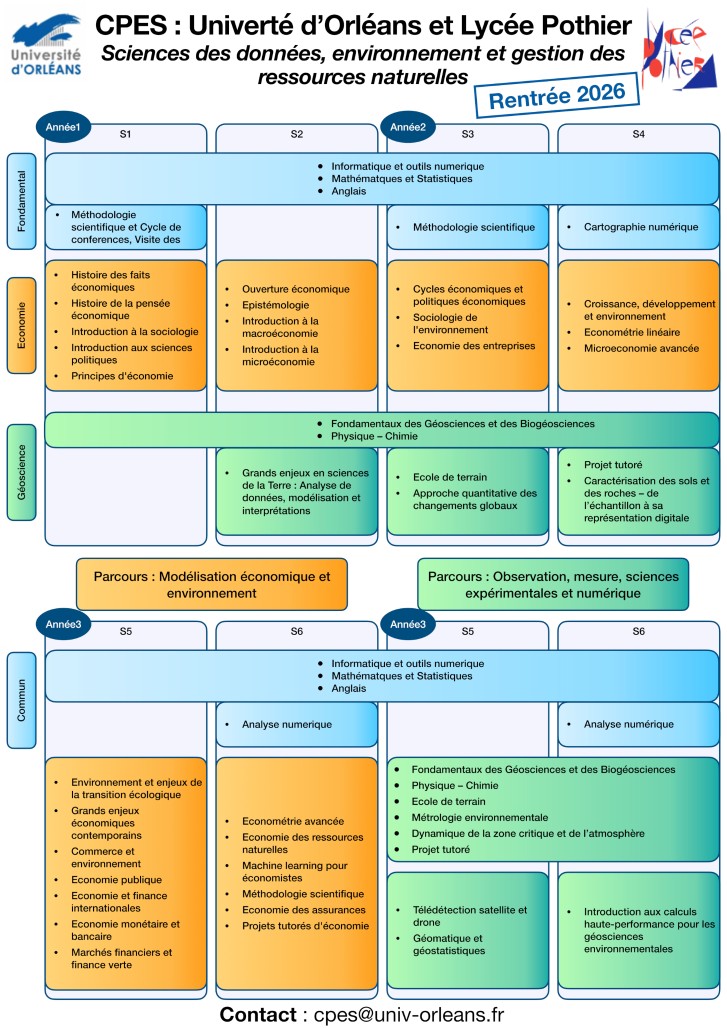
Téléchargez la présentation schématique de la maquette au format pdf
Admission
Conditions d'admission
Être titulaire d’un baccalauréat général
Cette formation a pour ambition d'accueillir de futurs bacheliers aux profils divers, partageant des savoirs et compétences solides, notamment en mathématiques.
Modalités d'inscription
Modalités d'inscription en licence pour les (futurs) bacheliers titulaires d'un bac français obtenu en France et s'inscrivant pour la 1ère fois : Fiche parcoursup de la licence CPES
Inscriptions en JUILLET dès les résultats d'obtention du baccalauréat selon les modalités communiquées lors de la pré-inscription.
Droits de scolarité
Pour les étudiants :
https://www.univ-orleans.fr/fr/univ/formation/droits-dinscriptions
Pour les adultes en reprise d'études, pour les contrats de professionnalisation et pour la VAE, consulter le SEFCO .
formulaire de contact
Pré-requis obligatoires
Les « attendus »
La nature de la formation implique que les candidats portent un intérêt à la variété des disciplines enseignées (économie, géosciences , informatique, ainsi que mathématiques et physique-chimie). Les mathématiques constituant un socle commun à l’ensemble des enseignements, le suivi minimum de la spécialité Mathématiques en première ou de l’option Mathématiques complémentaires en terminale est vivement conseillé. Il est également attendu des candidats une appétence pour les questions associées aux enjeux climatiques et économiques.
Éléments de cadrage national pour la licence mention Économie :
• Disposer de compétences mathématiques et statistiques indispensables à l'économie et à la gestion, ainsi qu'aux géosciences
Les enseignements qu'ils soient en économie ou en géosciences font fréquemment appel à la modélisation mathématique afin de mieux penser les problèmes étudiés et d'analyser les résultats qui en découlent de manière logique. De plus, une grande partie des métiers de l'économie et de la gestion, tout comme ceux des géosciences, s'appuient sur l'analyse de données chiffrées.
• Savoir mobiliser des compétences d'expression écrite et orale et de raisonnement logique afin de pouvoir argumenter un raisonnement conceptuel
Les enseignements d'économie et de géosciences requièrent que les étudiants soient capables de produire une argumentation structurée, même relativement simple (cette compétence ayant vocation à être renforcée à l'université) et à raisonner sur des concepts. La formation en licence requiert une certaine capacité d'abstraction, de logique formelle et de déduction.
Les métiers de l'économie impliquent fréquemment la rédaction d'études ou de rapports nécessitant une argumentation structurée, des capacités de synthèse et un bon niveau de langue.
• Disposer d'une culture générale
La réflexion en économie se nourrit de l'actualité économique, politique et sociétale. L'étudiant doit donc être en mesure de situer et comprendre les enjeux sociétaux liés aux thématiques abordées au cours de ses études.
• Disposer de compétences méthodologiques et comportementales afin d'être capable de travailler en autonomie et de manière responsable.
En licence, l'étudiant est acteur de sa formation et de sa réussite. Il doit donc notamment être capable d'organiser son travail, d'aller chercher les ressources à sa disposition et de rechercher les temps de travail collectifs.
• Disposer de compétences en langue anglaise
Nombreux sont les secteurs en économie où la documentation professionnelle et universitaire ainsi que les relations d'affaires reposent sur l'anglais. Des compétences dans cette langue sont donc essentielles. Il en est de même en géosciences, pour lesquelles la très grande majorité des ressources documentaires et des communications sont en anglais.
Éléments de cadrage national pour la licence mention Sciences de la Terre :
• Disposer de compétences scientifiques
Cette mention implique, en effet, d'avoir une capacité à analyser, poser une problématique et mener un raisonnement, une capacité d'abstraction, de logique et de modélisation et la maîtrise d'un socle de connaissances disciplinaires et des méthodes expérimentales associées.
• Disposer de compétences en communication
Cette mention nécessite en effet une capacité à communiquer à l'écrit et à l'oral de manière rigoureuse et adaptée, une aptitude à se documenter dans au moins une langue étrangère, prioritairement anglaise et une capacité à l'écrire et à la parler à un niveau B.
• Disposer de compétences méthodologiques et comportementales
Cette mention requiert une curiosité intellectuelle, une capacité à s'organiser et à conduire ses apprentissages et, enfin, une aptitude à programmer son travail personnel et à s'y tenir dans la durée.
Et après
Poursuite d'études
Masters ouverts en poursuite d’étude à l'Université d'Orléans :
Pour les étudiants ayant suivi le parcours Modélisation économique et environnement :
-
Économie Internationale
-
Économie, Statistique
-
Monnaie, Banque, Finance
Pour les étudiants ayant suivi le parcours Observation, mesure, sciences expérimentales et numérique :
-
Geodata : Sciences de la Terre & des Planètes, Environnement
-
Sites et Sols Pollués : Diagnostic Environnemental - Sciences de la Terre & des Planètes, Environnement
-
Chimie, Pollution, Risques, Environnement
Au-delà des masters de l'Université d'Orléans, ce CPES ambitionne de fournir aux étudiants toutes les connaissances et compétences nécessaires pour candidater à des masters sélectifs en France dans les domaines de l'économie (économie de l'environnement, économie de l'énergie, management de l'environnement, développement durable, économie des ressources naturelles…) et des géosciences (Sciences de la Terre & des Planètes, Environnement).
Insertion professionnelle
A la sortie des masters :
En économie, au sein du secteur privé, d'organisme publics ou d'organisations internationales : analyste de données, analyste risque/crédit, chargé d'affaires, chargé d'études internationales, chargé d'études RSE, chargé d'études risques climatiques, chargé d'études statistiques/actuarielles, chargé de missions, consultant, conjoncturiste, data scientist, économiste...
En géosciences : au sein du secteur privé, d'organismes publics ou d'organisations internationales : analyste de données, notamment avec un accent particulier porté sur la qualité des données lors de leur acquisition, chargé d'études dans l'analyse des risques et des dangers basée sur des données, gestion des archives de données environnementales…
Poursuite d'études possible en doctorat.
Le programme de formation du CPES intègre notamment une part d'enseignements à et par la recherche, à travers notamment une initiation à la recherche scientifique grâce à un adossement aux laboratoires de recherche en géosciences et économie


